Web Vitals Extensions Google Chrome
Google implemented Web Vital Extension to improve the experience for web users, which has three categories, LCP, FID, and CLF. Web Vitals are essential because they are part of the new Google algorithms, implemented in May 2021.
According to Google studies, web pages that meet the Core Vitals are 24 percent abandoned by users. The purpose of web vitals is to optimize website content so that it is more effective and easier to navigate for web users as well as web pages are free of issues when being displayed.
The use of core Web Vitals is to provide the potential to have a significant impact on your website's Search Engine Optimization. The three components of Core Web Vitals seek to solve are: How quickly does a page load? How fast does a page become interactive? How quickly does a page become stable?
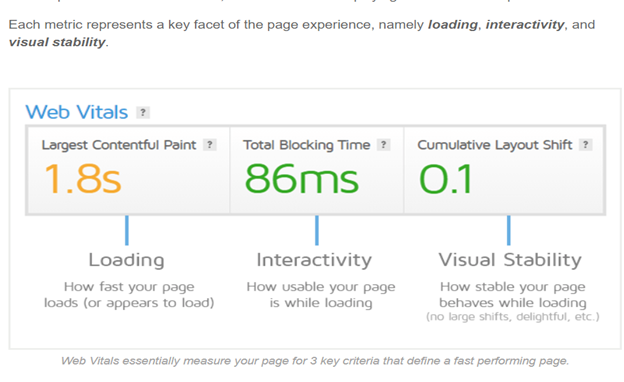
Google Web Vital Extension is a tool used to measure metrics for a healthy site. This is an extension to measure the Core Web Vitals, which provides fast feedback about how well websites perform when browsed.
This feedback is about how fast websites load, how much quality they have, and how the layout displays. To accomplish this, performance is run by google chrome vitals, which shows the report results on the experience, page speed, and search console.
The three main extensions used to read website performance are content paint, cumulative layout shift, and first input delay. Then, this extension is divided into three content features: The ambient badge, whose primary function is to check that websites are free of thresholds when passing through the core.
After the installation, red or green color is displayed to show how clean the URL is. The badge has three numbers: green, grey, and red. Reddit runs this extension and detects pages' performance, and updates will be applied to the read pages.

"Core Web Vitals are the subset of Web Vitals that apply to all web pages, should be measured by all site owners, and will be surfaced across all Google tools. Each Core Web Vitals represents a distinct facet of the user experience, is measurable in the field, and reflects the real-world experience of a critical user-centric outcome.
The metrics that makeup Core Web Vitals will evolve. The current settings for 2020 focus on three aspects of the user experience, loading, and visual stability, and includes the following metrics (and their respective thresholds)."
The three metrics used Largest Content Paint (LCP), First Input Delay (FID), and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS).
Largest Content Paint (loading)
The primary purpose of this is to see how quickly web pages download on the internet. It is an important metric used to measure perceived load speed. It marks the point in the page load timeline when the page's main content has loaded.
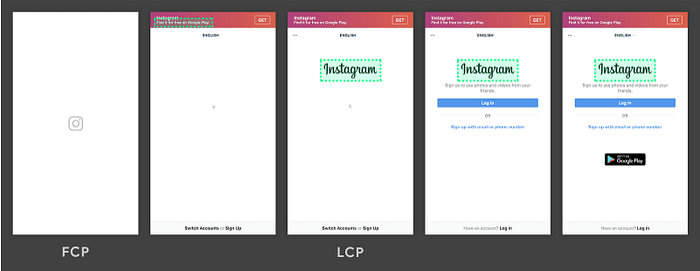
A fast LCP is fast is a sign that the website is quick to download. As taken from a source:
"Largest Content Paint is easy to understand- it is simply the time it takes for the largest element to appear on the screen. These elements might include images, videos, or other types of content."
Measuring content has been a challenge for web designers throughout history to ensure that content downloads fast and becomes visible to users. For a web page to be successful, it needs to be fast to download all its content. Also, it needs to respond to what the users see on screen. Web pages need to be simple.
The Largest Content Paint metric task reports the render time of the most prominent image or text block visible within the viewport. This is related to when the page started to get downloaded.
Sites must have a 2.5 second or less LCP to ensure users have a great experience opening websites on mobile or desktop devices. Some of the elements that need much content are images, videos, and links that contain pictures and videos.
LCP is dependent on FCP, which is an old metric. A primary function of LCP is to prevent errors displaying the CSS stylesheet or JavaScript. For example, when you run the code, it will show you what's in red or green, so if there are many code marks on the red color, you have to remove them.
Notably, the more code you have on your website, the longer the website will take to download.
First input Delay (Interactivity)
Metric used to measure load responsiveness that quantifies allows users have a great experience when they try to interact with unresponsive pages. This input makes users interact with websites and how pixels are displayed on the screen.
So, it comes to when users try to interact with those pixels that take place. As taken quoted next,
"The First Input Delay measures the time it takes for the browser to respond to the user's first interaction. The faster the browser reacts, the more responsive the page will appear."
First Input Delay measures the time when interacting on a website. It all goes from a link or simply clicking a button. It is using JavaScript, for example, that users can interact with. Sites should strive to have a First Input Delay of 100 milliseconds or less.
A good measure is just about the 75th percentile of page loads, segmented across mobile and desktop devices to ensure users have a good experience.
Cumulative layout Shift (Visual Stability)
It is an important metric to measure stability. Shift measures visual strength and quantifies the amount of unexpected layout shift of visible page content. It helps quantify how often users experience unexpected layout shifts. As quoted next,
"This metric tries to determine how 'stable' stuff loads onto your screen. It looks at how often stuff jumps around while loading and by how much."
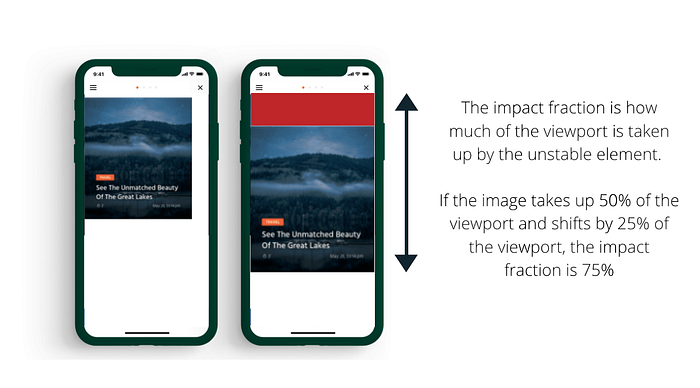
A low CLS helps ensure that the page works well. An excellent example of CLS is when you are reading information on a website and collapsed or changed to something else, which causes text to move.
Or for example, when you want to click a link and the link moved, you end up clicking on something else. This kind of lousy event happens when elements are added on top of other factors. In most cases, it is all related to the dimensions of images or content.
An example of this is third-party content that over displays on top of your main content. The CLS metric is the one that addresses this problem by measuring it and showing how often users experience these problems.
The CLS measures the total of all individual layout shift scores for every unexpected layout shift that occurs during the entire lifespan of the page. A layout shift occurs whenever a visible element changes its position from one rendered frame to the next.
Sites must have a CLS score of 0.1 or less to ensure users have a good experience. It is essential to avoid unexpected layout shifts by sticking to a few guiding principles: include size attributes on images and video elements and let space on CSS aspect ratio boxes. This way, browsers allocate suitable space for the download.
Also, don't insert content above already existing content. Additionally, animations should follow a sequence.
According to Google,
"If a website meets the "Good" criteria for all three Core Web Vitals metrics, users are 24% less likely to abandon. That's a massive number of potential leads, buyers, and clickers who will stick around on your website to take the desired action!"
Using Programs to run the code on Web sites.
To measure how well run your Web Vitals are on your or other websites, you can use a Google Search Console, Google PageSpeed, which shows information for Largest Content Paint (LCP), First Input Delay (FID), and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS).
An excellent way to know what implementations to add to your web page is to visit the most visited websites online. This will give you a clue about what a successful website should look like.
It is recommended to save all writing assistant programs on a specific file system. This will be helpful for you as a web developer when assigning the website you agree on.
Similar to Web Vitals, you can add another extension to your Google Chrome Search List.

To have access to these extensions, you have to create a Google Chrome account. After you have made your account, you have to visit the Chrome Web Store.
Once clicked on the link, you will see that there are many extensions. While many of those extensions are free, others have to be paid for to use them.
After you click on the link, extensions are displayed by title and area of interest so that users can decide which ones to use; for example, the ones recommended for you are shown on top. This is based on your Google Chrome history and what you use the most.
Other titles of interest are displayed as you scroll down are: Chrome Web Store Gems of 2020, Staying at Home, Editor's Picks, Work from Home, Online Education, Entertainment Center, Personalise Chrome, Chat with Chrome, and many more. Each one of these titles contains extensions that relate to its topic.
For example, if you want to personalize your Chrome background image, you can go to Personalize Chrome and click on View Earth from Google Chrome, displayed. As noticed, this extension is offered by Google Earth.
In this way, each extension is offered by its developer. A few of the characteristics shown once already on each extension are overview, privacy practices, reviews, support, and related. Also, on the left top, it is shown how many users are using this extension and stars number the rating.
Importantly, to the right bottom, additional information is displayed about the extension such as version, update, size, language, and developer. Most importantly, you can click Contact the developer if you need more information about the extension, and it will be taken to the email. Additionally, the address is provided.
After you have made sure about what extension you want, you can add it to Chrome. To do this, you have to click on the right top where it says Add to Chrome. A little window will pop up immediately with the options add extension or cancel. Click add, and it will be added on top of your Chrome web browser.
Once installed, you can always go back and say remove.
Takeaway
Optimizing a website is paramount when it comes to the user experience. But more importantly, digital marketing firms know that a well-structured website that meets the primary visitor's needs will significantly impact their SEO efforts.
